What is Google Speech-to-Text?
Google speech-to-text is a cloud-based API service that converts audio into written text using advanced machine learning models. Developed by Google Cloud, this google automatic speech recognition system processes spoken words from audio files or real-time streams and produces accurate text transcriptions.
The service leverages Google’s decades of AI research and is the same technology powering Google Assistant, YouTube captions, and Google Meet transcriptions. Cloud speech to text operates entirely on Google’s cloud infrastructure, requiring no local processing power or specialized hardware.
Key capabilities include support for 125+ languages and variants, real-time streaming recognition, batch file transcription, speaker diarization (identifying different speakers), automatic punctuation, profanity filtering, and custom vocabulary adaptation. The system handles various audio sources including phone calls, videos, voice commands, podcasts, and meetings.
Google’s speech-to-text works through REST API calls or gRPC streaming, making it accessible to developers across web applications, mobile apps, IoT devices, and enterprise systems. The service processes audio in multiple formats including FLAC, WAV, MP3, and OGG.
Why We Use Google Speech-to-Text
Industry-Leading Accuracy: Google cloud speech-to-text achieves 95%+ word accuracy on clear audio in supported languages, surpassing most competitors. The system continuously improves through machine learning on billions of voice samples.
Massive Language Support: Supports 125+ languages and dialects including English variants (US, UK, Australian, Indian), Spanish (multiple regional variants), Mandarin, Hindi, Arabic, Japanese, and many others with native pronunciation understanding.
Real-Time and Batch Processing: Process live audio streams with low latency (as fast as 300 milliseconds) for real-time applications, or submit audio files for batch transcription. Flexibility suits different use cases.
Scalable Cloud Infrastructure: Handles everything from single API calls to millions of requests daily. Google’s infrastructure automatically scales without requiring capacity planning or server management.
Advanced Features: Automatic punctuation, speaker identification, word-level timestamps, profanity filtering, and model adaptation for domain-specific vocabulary improve transcription quality and usefulness.
Cost-Effective Pricing: Pay only for actual usage with no minimum fees or upfront costs. Free tier includes 60 minutes monthly. Pricing scales with volume and features used.
Enterprise Security: Complies with major security standards including SOC 2/3, ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR. Audio data encrypted in transit and at rest with enterprise-grade security.
Easy Integration: Well-documented APIs with client libraries for Python, Java, Node.js, Go, Ruby, PHP, and .NET. Quick implementation for developers familiar with REST APIs or gRPC.
Continuous Improvement: Models automatically update with latest improvements. No manual updates or maintenance required to benefit from accuracy enhancements.
How to Use Google Speech-to-Text: Step-by-Step Method
Setting Up Google Cloud Account
- Create Google Cloud Account: Visit cloud.google.com and sign up. New users receive $300 in free credits valid for 90 days, plus ongoing free tier of 60 minutes monthly transcription.
2. Create Project: In Google Cloud Console, create a new project to organize your Speech-to-Text resources. Each project gets separate billing, quotas, and API access.
3. Enable Speech-to-Text API: Navigate to API Library, search for “Cloud Speech-to-Text API,” and click “Enable.” This activates the service for your project.
4. Create Service Account: Generate authentication credentials by creating a service account. Download the JSON key file which contains credentials for API authentication.
5. Set Environment Variable: Store the service account key path in GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS environment variable. This authenticates your API requests automatically
Basic Transcription (Synchronous Recognition)
For Audio Files Under 60 Seconds: Use synchronous recognition for quick results. Upload audio file or provide Cloud Storage URL, specify language code, and receive complete transcription in single API response.
Python Example:
from google.cloud import speech
client = speech.SpeechClient()
with open(“audio.wav”, “rb”) as audio_file:
content = audio_file.read()
audio = speech.RecognitionAudio(content=content)
config = speech.RecognitionConfig(
encoding=speech.RecognitionConfig.AudioEncoding.LINEAR16,
sample_rate_hertz=16000,
language_code=”en-US”,
)
response = client.recognize(config=config, audio=audio)
for result in response.results:
print(result.alternatives[0].transcript)
Long Audio Transcription (Asynchronous Recognition)
For Files Over 60 Seconds: Use asynchronous recognition for longer audio. Upload file to Google Cloud Storage first, submit transcription request, receive operation ID, and poll for results or use callback webhook.
Process: Upload audio to Cloud Storage bucket, create recognition request with storage URI, call long_running_recognize method, check operation status periodically, and retrieve complete transcript when finished (typically takes 30-50% of audio duration).
Real-Time Transcription (Streaming Recognition)
For Live Audio: Stream audio data to API in real-time and receive partial transcription results as speech occurs. Essential for live captions, voice commands, and interactive applications.
Implementation: Open streaming session, send audio chunks (recommended 100ms intervals), receive interim results as user speaks, get final results when speech pause detected, and handle continuous conversation with multiple utterances.
Use Cases: Live meeting transcription, voice-controlled interfaces, real-time subtitling for broadcasts, interactive voice assistants, and phone call transcription.
Advanced Configuration Options
Speaker Diarization: Enable speaker identification to distinguish between multiple speakers in audio. Google to text automatically labels segments as Speaker 1, Speaker 2, etc. Useful for interviews, meetings, and multi-person conversations.
Enable Feature:
diarization_config = speech.SpeakerDiarizationConfig(
enable_speaker_diarization=True,
min_speaker_count=2,
max_speaker_count=5,
)
Automatic Punctuation: Add enable_automatic_punctuation=True to configuration for proper sentence structure, commas, periods, and question marks without manual editing.
Word Timestamps: Get precise timing for each word spoken, enabling synchronized captions, audio editing interfaces, and searchable transcripts with jump-to-word functionality.
Profanity Filtering: Automatically replace profane words with asterisks in family-friendly applications or content moderation scenarios.
Speech Adaptation: Provide custom vocabulary or phrases to improve recognition of domain-specific terms like product names, technical jargon, or proper nouns.
Using Enhanced Models
Phone Call Model: Optimized for 8kHz audio typical of phone systems. Improves accuracy for telephony applications, call centers, and voicemail transcription.
Video Model: Tuned for multiple speakers, background noise, and varied audio quality common in video content. Best for YouTube captions and video editing.
Command and Search Model: Optimized for short queries, voice commands, and search terms. Lower latency for interactive applications.
Medical Conversations Model: Specialized vocabulary for healthcare discussions, medical terminology, and clinical documentation (requires additional compliance verification).
Handling Different Audio Formats
Supported Formats: FLAC (lossless, preferred), WAV (uncompressed), MP3 (lossy compression), OGG Opus (efficient for streaming), and AMR (mobile telephony).
Audio Requirements: Sample rate between 8kHz-48kHz (16kHz recommended), mono or stereo channels (mono preferred for speech), appropriate bit depth, and clear audio without excessive noise or distortion.
Pre-Processing Tips: Normalize audio levels, remove background music when possible, use noise reduction cautiously (don’t over-process), and convert to supported format before submission.
Integration Patterns
Direct API Integration: Call REST API directly from applications using HTTP requests. Simple for web services and scripting.
Client Libraries: Use official Google Cloud client libraries for cleaner code, automatic retries, authentication handling, and error management.
Third-Party Tools: Integrate with tools like Twilio for phone transcription, Zoom for meeting captions, or streaming platforms for live broadcast subtitles.
Webhook Callbacks: Configure callbacks for asynchronous operations to avoid polling, enabling event-driven architectures.
Pricing Structure
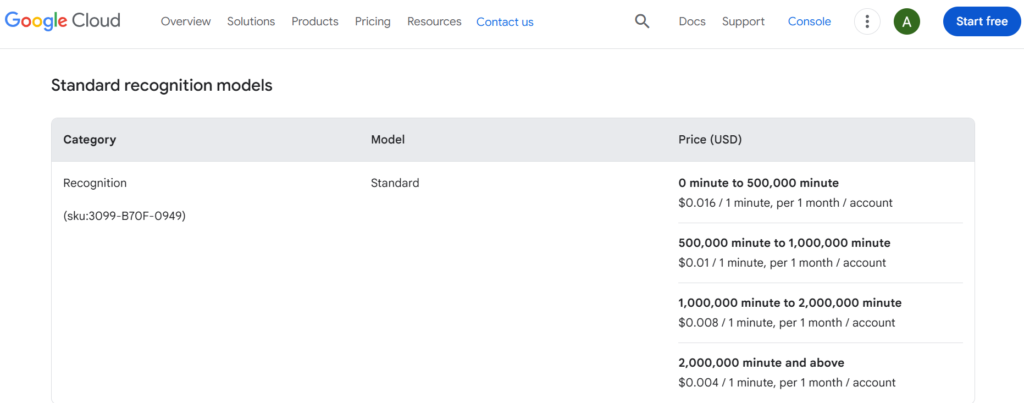
Free Tier: 60 minutes of transcription per month using standard models. Applies to all recognition types (synchronous, asynchronous, streaming).
Standard Models:
- 0-60 minutes: Free
- 60-1 million minutes: $0.006 per 15 seconds ($1.44/hour)
- 1+ million minutes: $0.004 per 15 seconds ($0.96/hour)
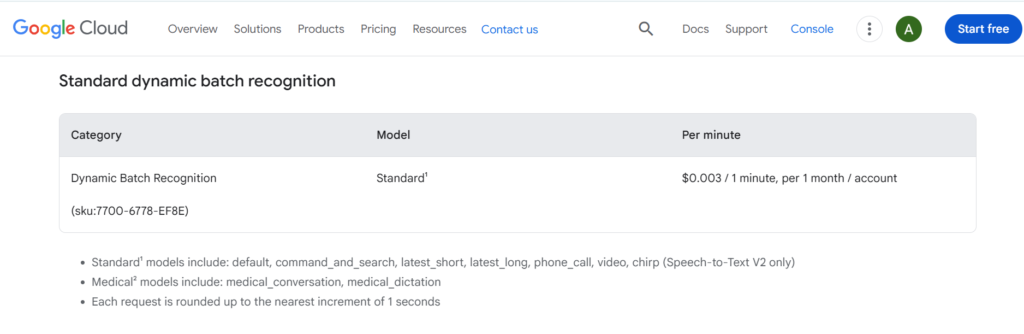
Enhanced Models (phone call, video):
- $0.009 per 15 seconds ($2.16/hour)
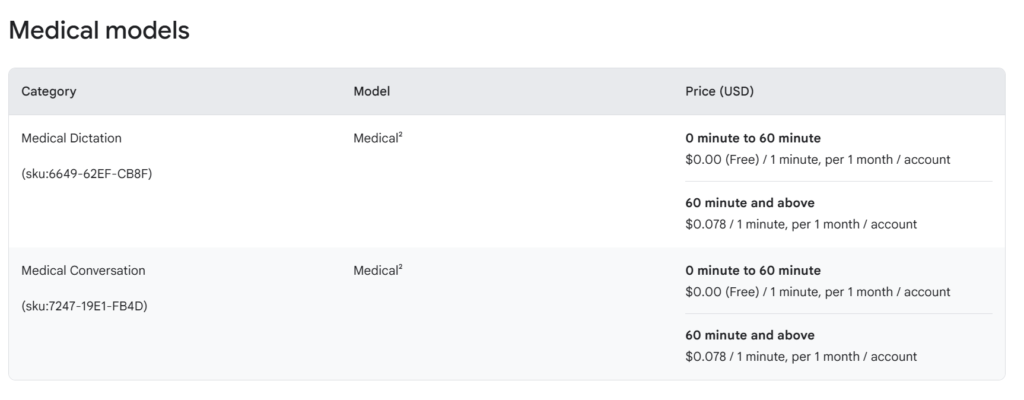
Medical Conversation Model:
- $0.018 per 15 seconds ($4.32/hour)
Data Logging Discount: Opt-in to allow Google to log audio data for model improvement and receive 50% pricing discount. Audio automatically deleted after analysis.
Additional Features: Speaker diarization, word timestamps, and automatic punctuation included at no extra cost. Speech adaptation for custom vocabulary is free.
Use Cases and Applications
Call Center Analytics: Transcribe customer service calls for quality assurance, sentiment analysis, keyword extraction, and agent training. Automated transcription enables analyzing thousands of calls efficiently.
Meeting Transcription: Automatically transcribe video conferences, board meetings, interviews, and discussions for documentation, searchability, and accessibility compliance.
Media and Entertainment: Generate captions for videos, create searchable podcast transcripts, subtitle streaming content, and enable voice search in media libraries.
Voice Commands: Power voice-controlled applications, smart home devices, automotive interfaces, and IoT products with accurate speech recognition.
Healthcare Documentation: Transcribe doctor-patient conversations, medical dictation, clinical notes, and telemedicine sessions (requires HIPAA compliance configuration).
Legal and Compliance: Transcribe depositions, court proceedings, legal consultations, and compliance recordings with timestamp accuracy for documentation.
Education: Create lecture transcripts, enable accessible course materials, power language learning applications, and facilitate note-taking assistance.
Accessibility: Provide real-time captions for deaf or hard-of-hearing individuals in live events, broadcasts, video content, and communication platforms.
Limitations of Google Speech-to-Text
Technical Limitations
Audio Length Restrictions: Synchronous recognition limited to 60 seconds. Longer audio requires asynchronous processing or streaming, adding complexity to simple use cases.
Processing Time: Asynchronous operations take 30-50% of audio duration to complete. Not suitable for ultra-low-latency requirements beyond streaming mode.
Streaming Duration Limits: Streaming sessions limited to 5 minutes per request. Long conversations require handling multiple streaming sessions with connection management.
File Size Constraints: Audio files must be under 10MB for direct API requests. Larger files require Google Cloud Storage upload, adding infrastructure complexity.
Sample Rate Requirements: Audio between 8kHz-48kHz only. Lower or higher sample rates rejected, requiring pre-processing or resampling.
Accuracy Limitations
Background Noise Sensitivity: Accuracy degrades significantly with background noise, multiple simultaneous speakers, or poor audio quality. Requires relatively clean audio for best results.
Accent Variations: While supporting many languages, accuracy varies with accents, dialects, and non-native speakers not well-represented in training data.
Domain-Specific Terms: Technical jargon, brand names, proper nouns, and specialized vocabulary often misrecognized without speech adaptation configuration.
Homophones and Context: May confuse similar-sounding words (their/there, to/too) without sufficient context, requiring manual review for critical applications.
Crosstalk Issues: Multiple simultaneous speakers or overlapping speech significantly reduces accuracy even with speaker diarization enabled.
Cost Considerations
No Unlimited Plans: Pay-per-use pricing with no flat-rate unlimited option. High-volume applications can incur significant costs (1000 hours = $1,440-$2,160).
Enhanced Model Costs: Premium models (video, phone call, medical) cost 50-200% more than standard models. Budget planning required for large-scale deployments.
Data Egress Charges: Transferring large audio files to Cloud Storage incurs storage and egress costs separate from transcription pricing.
Free Tier Limitations: 60-minute monthly limit insufficient for most production applications. Easy to exceed accidentally during development and testing.
Integration Limitations
Internet Dependency: Requires stable internet connection with sufficient bandwidth. No offline processing capability for sensitive or disconnected environments.
Cloud Storage Requirement: Long audio files must be uploaded to Google Cloud Storage, requiring additional service setup and access management.
Authentication Complexity: Service account setup and key management add security considerations and deployment complexity versus simple API keys.
Regional Availability: Some advanced features or models only available in specific Google Cloud regions, potentially increasing latency for global applications.
Data Privacy Concerns
Audio Data Transmission: All audio must be sent to Google’s servers for processing. Not suitable for highly sensitive or classified information without compliance review.
Data Logging Options: Opting into data logging (for 50% discount) allows Google to analyze and store audio data for model improvement, raising privacy concerns.
Retention Policies: Unclear long-term data retention despite stated deletion policies. Audit trail requirements may be insufficient for regulated industries.
Third-Party Access: Reliance on Google as third-party processor requires vendor risk assessment and potential data processing agreements for compliance.
Feature Limitations
No Punctuation Control: Cannot customize punctuation style or disable specific marks. Automatic punctuation occasionally incorrect for specialized content formats.
Limited Speaker Identification: Speaker diarization labels speakers numerically only. Cannot identify speakers by name or match against voice profiles automatically.
No Emotion Detection: Transcribes words only without detecting emotional tone, sarcasm, or sentiment in speech. Requires separate sentiment analysis tools.
Single Language Per Request: Cannot automatically detect or handle code-switching between languages within single audio file. Requires language specification upfront.
Operational Limitations
API Quotas: Default quotas limit concurrent requests and monthly usage. Quota increases require manual request and approval, causing delays for scaling.
No Batch Discounts: Pricing remains per-minute regardless of volume within pricing tiers. No enterprise discounts or volume commitments beyond standard tiers.
Limited Customization: Cannot train fully custom models on proprietary data. Speech adaptation helps but doesn’t match dedicated custom model performance.
Version Control: Automatic model updates improve accuracy but may change output format or behavior without warning, potentially breaking dependent applications.
Best Practices for Optimal Results
Audio Quality: Use high-quality microphones, record in quiet environments, maintain consistent audio levels, use lossless formats when possible, and remove background music that interferes with speech.
Proper Configuration: Specify correct language code and region, enable automatic punctuation, use appropriate model (phone call, video, default), set reasonable speaker count for diarization, and provide speech adaptation hints for special vocabulary.
Error Handling: Implement retry logic with exponential backoff, handle quota exceeded errors gracefully, validate audio format before submission, monitor API response times, and log errors for troubleshooting.
Cost Optimization: Use standard models unless enhanced features necessary, enable data logging for 50% discount if privacy permits, batch process audio when real-time not required, optimize audio compression without sacrificing quality, and monitor usage to avoid unexpected costs.
Testing Strategy: Test with representative audio samples, verify accuracy across different speakers and accents, validate special vocabulary recognition, test error handling with poor audio, and benchmark latency for time-sensitive applications.
Alternatives to Consider
Amazon Transcribe: AWS alternative with similar features and pricing. Better for organizations already using AWS infrastructure.
Microsoft Azure Speech: Competitive accuracy with strong Windows ecosystem integration and custom model training capabilities.
Assembly AI: Simpler API focused on developer experience with additional features like content moderation and entity detection.
Rev.ai: Human-in-the-loop option combining AI transcription with human review for highest accuracy requirements.
Whisper (OpenAI): Open-source alternative deployable on-premises for privacy-sensitive applications, though requiring significant technical expertise.
Conclusion
Google speech-to-text represents the gold standard in cloud-based transcription services, offering unmatched accuracy, scalability, and language support. The service’s advanced machine learning models, built on Google’s decades of AI research, deliver reliable results for applications ranging from simple audio transcription to complex real-time voice interfaces.
Understanding the limitations around audio length restrictions, cost considerations, and privacy implications helps developers make informed decisions about implementation. While the pay-per-use pricing can add up for high-volume applications, the free tier and scalable infrastructure make it accessible for projects of all sizes.
Whether you’re building voice-controlled applications, transcribing customer service calls, adding captions to video content, or creating accessible meeting transcripts, google cloud speech-to-text provides the tools and infrastructure needed for professional audio-to-text conversion. The service’s continuous improvement through machine learning ensures your applications benefit from accuracy enhancements without requiring manual updates or model retraining.
For organizations requiring enterprise-grade transcription with industry-leading accuracy and comprehensive language support, Google automatic speech recognition delivers proven results that justify the investment in cloud-based voice processing infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions
Google speech-to-text is a cloud-based API that converts spoken audio into written text using AI. It processes audio files or live streams and produces accurate transcriptions supporting 125+ languages.
Google cloud speech-to-text achieves 95%+ accuracy on clear audio in supported languages. Accuracy depends on audio quality, speaker clarity, background noise, and language complexity.
Google speech-to-text includes 60 free minutes monthly. Standard pricing is $0.006 per 15 seconds ($1.44/hour) for minutes 60-1 million. Enhanced models cost $0.009 per 15 seconds ($2.16/hour).
Google automatic speech recognition supports 125+ languages including English (multiple accents), Spanish, Mandarin, Hindi, Arabic, Japanese, French, German, Portuguese, Russian, and many regional variants.
Yes, streaming recognition enables real-time transcription with latency as low as 300 milliseconds. Perfect for live captions, voice commands, and interactive applications requiring immediate feedback.
Create Google Cloud account, enable Speech-to-Text API, generate service account credentials, install client library, and call API with audio data and configuration options. Comprehensive documentation available.
Yes, speaker diarization feature automatically identifies and labels different speakers in audio. Set min/max speaker count in configuration, and results include speaker labels for each utterance.
Supported formats include FLAC, WAV, MP3, OGG Opus, and AMR. Sample rates must be 8kHz-48kHz with 16kHz recommended. Both mono and stereo supported, with mono preferred.
No, Google speech-to-text requires internet connection and processes audio on Google’s cloud servers. No offline or on-premises deployment option available for standard service.
Yes, Google cloud speech-to-text can be configured for HIPAA compliance with appropriate Business Associate Agreement. Use medical conversation model and proper Cloud configuration for healthcare applications.
Synchronous recognition returns results immediately for audio under 60 seconds. Asynchronous processing typically completes in 30-50% of audio duration. Streaming provides real-time results.
Yes, speech adaptation allows providing custom phrases and vocabulary to improve recognition of domain-specific terms, product names, technical jargon, and proper nouns.
Synchronous recognition limited to 60 seconds. Asynchronous recognition handles audio up to 480 minutes (8 hours). Streaming sessions limited to 5 minutes per connection but can be chained.
By default, Google processes and deletes audio data after transcription. Opting into data logging allows Google to store audio for model improvement in exchange for 50% pricing discount.
No, you must specify one language per request. Cannot automatically detect or handle code-switching between languages within single audio file. Process separately for multilingual content.



